Table of contents
Part 1 - Forex Market Trading Hours and Sessions
Part 2 - Key Market Participants and Their Influence on Forex Trading Hours
Part 3 - Economic Indicators That Impact Forex Market Movements
Part 4 - Trading Strategies Optimized for Different Forex Market Hours
Part 5 - Order Execution and Liquidity Variations by Forex Market Timing
The global currency market operates around the clock, providing opportunities for traders across different time zones. The forex market follows a decentralized structure, with major financial centers opening and closing at specific hours, creating distinct trading sessions. Understanding when these sessions begin and how they overlap is essential for identifying high-liquidity periods and potential trading opportunities. The timing of market openings influences price movements, volatility levels, and the overall trading environment, making it a critical factor for anyone engaging in currency exchange. Recognizing these timeframes helps traders optimize their strategies and align their activities with the most active market conditions.
Forex Market Trading Hours and Sessions
The timing of forex trading sessions is a critical factor that influences price movements, liquidity, and overall market volatility. Different financial centers operate on distinct schedules, impacting how currencies such as the US Dollar, Euro, Japanese Yen, and British Pound fluctuate throughout the day. Understanding these trading hours allows retail traders, hedge funds, and commercial banks to align their strategies with peak activity periods, ensuring optimal trade execution.

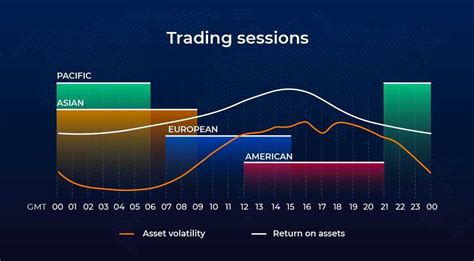
Global Forex Market Open and Close Times
Forex operates 24 hours a day, driven by major financial hubs worldwide. These sessions ensure continuous market activity, providing traders with numerous opportunities.
Sydney Session (Opens: 22:00 GMT, Closes: 07:00 GMT) – The first session to open, influencing the Australian Dollar and New Zealand Dollar liquidity.
Tokyo Session (Opens: 00:00 GMT, Closes: 09:00 GMT) – The Japanese Yen sees significant activity as Asia’s largest market operates.
London Session (Opens: 08:00 GMT, Closes: 17:00 GMT) – The most liquid session, dominated by British Pound, Euro, and Swiss Franc trades.
New York Session (Opens: 13:00 GMT, Closes: 22:00 GMT) – The final major session, driving volatility in US Dollar pairs.
Session Overlaps and High Liquidity Periods
Certain timeframes experience increased liquidity and volatility due to overlapping trading hours. These moments provide the best execution conditions for day trading, news trading, and scalping strategies.
Tokyo-London Overlap (08:00 GMT - 09:00 GMT)
Moderate liquidity as Asian traders transition out of the market.
Influences Japanese Yen, Chinese Yuan, and Australian Dollar movements.
London-New York Overlap (13:00 GMT - 17:00 GMT)
The most active forex period, with central banks, hedge funds, and corporations executing large orders.
High-impact economic data such as interest rate decisions, unemployment rates, and GDP growth are released.
Sydney-Tokyo Overlap (00:00 GMT - 02:00 GMT)
Focuses on Australian Dollar, New Zealand Dollar, and Japanese Yen.
Less volatile compared to London-New York but crucial for traders in the Asia-Pacific region.
Best Time to Trade Forex for Different Strategies
Trading strategies vary in effectiveness depending on market hours and liquidity conditions.
| Trading Strategy | Best Time to Trade | Key Currencies Impacted |
|---|---|---|
| Day Trading | London-New York Overlap | US Dollar, Euro, British Pound |
| Swing Trading | New York Close to Asian Open | Australian Dollar, Japanese Yen |
| Scalping | High-volatility hours | Swiss Franc, Euro, US Dollar |
| Carry Trade | Tokyo Session | Japanese Yen, Australian Dollar |
| News Trading | Before and after economic releases | US Dollar, British Pound, Euro |
Selecting the right session ensures alignment with preferred order types like market orders, stop loss orders, and take profit orders for effective trade execution.
Weekend Trading: What Happens When the Market Closes?
Forex trading stops on Friday at 22:00 GMT and resumes on Sunday at 22:00 GMT. The closure period creates unique market behaviors:
Price Gaps on Monday Open – Currencies like the British Pound and Canadian Dollar may open at significantly different levels from Friday’s close due to news events.
Interest Rate Accruals – Traders holding positions over the weekend are affected by interest rate differentials, influencing carry trade strategies.
Central Bank Announcements – Some key policies or interventions occur outside trading hours, impacting Monday’s volatility.
Managing exposure before the weekend is essential to avoid unexpected movements when the market reopens.
Impact of Public Holidays on Forex Market Hours
National holidays in major economies impact forex trading liquidity and price fluctuations.
US Dollar Volatility on Independence Day (July 4th) – Reduced trading activity in the New York session.
Euro and British Pound Liquidity Drops on Christmas (December 25th) – London and European markets remain closed, leading to thin trading conditions.
Japanese Yen Sensitivity During Golden Week (April 29 - May 5) – The Tokyo session sees significantly reduced participation from institutional traders.
Chinese Yuan and Trade Balance Announcements Post-Chinese New Year – Market volatility increases as trading volume normalizes.
Understanding public holiday schedules ensures traders adapt their technical indicators, such as moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and Fibonacci retracements, for more effective analysis.
Key Market Participants and Their Influence on Forex Trading Hours
The forex market operates through a network of participants who contribute to liquidity, price movements, and volatility. Central banks, commercial banks, hedge funds, brokers, and retail traders each play a role in shaping trading hours and market activity. Their interactions determine fluctuations in major currency pairs like the US Dollar, Euro, British Pound, and Japanese Yen, making market timing a crucial factor for traders.
Central Banks and Their Role in Forex Market Timing
Central banks such as the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of Japan influence forex trading hours through monetary policy decisions. Their actions impact interest rates, currency stability, and overall liquidity.
Interest Rate Announcements: Scheduled rate decisions cause volatility, affecting trading strategies like carry trade and news trading.
Foreign Exchange Interventions: Direct market interventions impact liquidity in pairs involving the Japanese Yen, Swiss Franc, and Canadian Dollar.
Economic Data Releases: Reports such as GDP growth, inflation rate, and unemployment rate influence market sentiment during high-volume sessions.
Policy Speeches: Public addresses from central bank officials create speculative movements, particularly in sessions where major economic centers overlap.
Traders monitor central bank activities to anticipate currency fluctuations and adjust their stop loss orders, market orders, and limit orders accordingly.
Commercial Banks and Liquidity Distribution Across Sessions
Commercial banks are the backbone of forex liquidity, facilitating cross-border transactions and institutional trading. Their participation varies based on regional market hours.
| Region | Major Commercial Banks | Peak Liquidity Period | Key Currency Pairs |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | JPMorgan, Citibank, Goldman Sachs | London-New York Overlap | USD/EUR, USD/JPY, USD/GBP |
| Europe | Deutsche Bank, Barclays, HSBC | London Session | EUR/GBP, EUR/USD, GBP/CHF |
| Asia-Pacific | Mitsubishi UFJ, ANZ, ICBC | Tokyo Session | JPY/USD, AUD/JPY, NZD/USD |
| Middle East | Qatar National Bank, First Abu Dhabi Bank | Sydney-Tokyo Overlap | USD/AED, EUR/JPY, GBP/USD |
The presence of commercial banks in different trading hours affects scalping, range trading, and swing trading strategies, as liquidity conditions determine the efficiency of trade execution.
Retail Traders vs. Institutional Investors: How Market Timing Differs
Market behavior varies between retail traders and large investment managers, hedge funds, and pension funds. Their trading hours, strategies, and capital influence price trends in different sessions.
Retail Traders:
Primarily active during the London and New York sessions due to high liquidity.
Prefer day trading, algorithmic trading, and news trading strategies.
Execute stop-loss and take-profit orders around major economic events.
Institutional Investors:
Trade large volumes, affecting price action during session transitions.
Use carry trade and trend-following strategies, holding positions over long periods.
React to macroeconomic indicators like trade balance and producer price index.
Institutional dominance during session overlaps dictates the flow of Australian Dollar, British Pound, and Swiss Franc, making liquidity shifts a key aspect of trade timing.
Brokers’ Trading Hours and Their Effect on Execution Speeds
Forex brokers operate around the clock but adjust spreads and order execution speeds based on market liquidity. Weekend trading gaps, session transitions, and economic data releases influence price spreads and order execution.
Spreads and Volatility:
Tight spreads during the London-New York overlap, suitable for scalping and day trading.
Wider spreads in low-liquidity periods, such as the Sydney session opening.
Execution Speed and Market Conditions:
Limit orders and stop-loss orders execute faster during high-volume sessions.
Slippage risk increases during major geopolitical events like Brexit, elections, and trade wars.
Understanding broker behavior ensures efficient trade execution and minimizes risks associated with order delays, liquidity drops, and price slippage.
Economic Indicators That Impact Forex Market Movements
Market movements in forex are driven by key economic indicators that affect liquidity, volatility, and trading strategies. Announcements related to inflation rate, interest rate, GDP growth, and unemployment rate directly influence the valuation of major currencies like the US Dollar, Euro, British Pound, and Japanese Yen. Understanding how these economic events align with forex market hours helps retail traders, hedge funds, commercial banks, and central banks optimize their trading strategies and execution timing.
Inflation Rate Announcements and Market Reactions
Inflation reports are among the most closely monitored indicators, as they provide insight into purchasing power and monetary policy expectations.
Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) are the most widely used inflation metrics.
Higher inflation rates often lead to central banks tightening monetary policy by raising interest rates, strengthening currencies like the US Dollar, British Pound, and Euro.
Lower inflation rates may trigger interest rate cuts, weakening demand for currencies such as the Japanese Yen and Swiss Franc.
Market reaction timing: Inflation reports from key economies, including the United States, Eurozone, and Japan, generate significant price movements in the London and New York trading sessions.
Traders often employ news trading strategies, trend following, and carry trade strategies to capitalize on inflation-induced volatility, using technical indicators like Bollinger Bands, Fibonacci retracement levels, and Moving Averages for analysis.
Interest Rate Decisions and Their Timing Across Sessions
Interest rate decisions by central banks such as the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, and Bank of England influence forex trading hours and overall market volatility.
| Central Bank | Announcement Frequency | Major Currency Pairs Affected | Key Trading Session | Impact on Forex Market |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Reserve (Fed) | Monthly | USD/EUR, USD/JPY, USD/GBP | New York | Causes sharp movements due to global reliance on the US economy |
| European Central Bank | Monthly | EUR/USD, EUR/GBP, EUR/JPY | London | High-impact due to Eurozone economic significance |
| Bank of Japan | Quarterly | JPY/USD, JPY/AUD, JPY/EUR | Tokyo | Yen volatility spikes due to carry trade adjustments |
| Bank of England | Monthly | GBP/USD, GBP/EUR, GBP/JPY | London | Moves British Pound, affecting trade balances and financial markets |
Forex traders adjust stop-loss orders, limit orders, and take-profit levels before interest rate announcements to mitigate risk. The largest price fluctuations typically occur in London and New York sessions, where institutional investors and hedge funds react to central bank policies.
GDP Growth Reports and Forex Market Timing
GDP reports provide a snapshot of a country’s economic performance and directly impact currency valuations.
Strong GDP Growth:
Supports a stronger currency by increasing investor confidence in the economy.
US Dollar, British Pound, and Australian Dollar often strengthen after positive GDP reports.
Weak GDP Growth:
Signals economic slowdowns, weakening demand for local currency.
Japanese Yen and Swiss Franc may benefit as safe-haven assets.
Market Timing & Liquidity Impact:
GDP reports are typically released during London and New York sessions, generating major price movements.
Volatility is highest in USD, GBP, and EUR pairs, influencing day trading and algorithmic trading strategies.
GDP and Other Indicators:
Closely linked to Manufacturing PMI and Retail Sales data, which provide further insight into economic momentum.
Investors watch GDP trends to anticipate interest rate decisions and adjust their trading strategies, including swing trading and carry trades accordingly.

Trading Strategies Optimized for Different Forex Market Hours
Different forex trading strategies align with specific market hours due to variations in liquidity, volatility, and economic event releases. Timing plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of day trading, swing trading, and news trading, as each approach benefits from different session characteristics. Understanding how forex market hours impact trade execution allows retail traders, hedge funds, and commercial banks to optimize their positions.
Day Trading: Best Market Hours for Quick Trades
Day traders rely on short-term price movements and high liquidity to execute multiple trades within a single session. The best hours for day trading coincide with peak volatility and session overlaps.
London-New York Overlap (13:00 – 17:00 GMT):
The most volatile period, driven by US Dollar, Euro, and British Pound pairs.
Economic reports such as GDP growth, trade balance, and retail sales impact price swings.
Asian Market Open (00:00 – 03:00 GMT):
High liquidity for Japanese Yen, Australian Dollar, and Chinese Yuan pairs.
Ideal for scalping and algorithmic trading due to stable price action.
Post-Economic Data Release Windows:
Interest rate decisions from central banks cause major intraday fluctuations.
Best for traders using news trading and momentum-based strategies.
Day traders monitor technical indicators such as Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD to identify trade opportunities during high-volume periods.
Swing Trading: Why Market Openings and Closures Matter
Swing traders capitalize on multi-day price fluctuations, often holding positions for days or weeks. Market openings and closures influence their strategies by providing key entry and exit points.
Market Openings:
The London session opening introduces increased liquidity, setting the trend for the day.
The New York session opening builds on London momentum, influencing high-impact currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD.
Session Closures and Overnight Gaps:
The New York close is critical for positioning trades ahead of the Asian session.
Overnight gaps, especially on Monday opens, impact swing traders analyzing weekend price movements.
Ideal Currency Pairs for Swing Trading:
EUR/USD and GBP/USD due to strong session trends.
USD/JPY and AUD/USD for capturing Asia-Pacific market influences.
Swing traders use Fibonacci retracement, Bollinger Bands, and Stochastic Oscillator to set trade parameters before market shifts.
News Trading: Maximizing Market Openings and Key Announcements
News trading focuses on capitalizing on price movements triggered by scheduled economic events. Understanding market timing is crucial for executing this strategy effectively.
| Key Economic Event | Optimal Trading Session | Major Currency Pairs Affected | Impact on Market |
|---|---|---|---|
| US Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) | New York Session (13:30 GMT) | USD/EUR, USD/JPY, USD/GBP | High volatility and sharp price reversals |
| Interest Rate Announcements | London & New York Sessions | GBP/USD, EUR/USD, AUD/USD | Increased liquidity and directional trends |
| Inflation Rate Reports (CPI, PPI) | Tokyo & London Sessions | USD/JPY, EUR/USD, GBP/CHF | Strong momentum trades with breakouts |
| Geopolitical Events (Brexit, Elections, Sanctions) | Varies (Unpredictable) | GBP/USD, EUR/JPY, USD/CAD | Unstable price action, gap risks, and market uncertainty |
News traders react quickly to economic releases by placing market orders, stop-loss orders, and trailing stop orders to capture volatility while managing risk.
Order Execution and Liquidity Variations by Forex Market Timing
Forex market liquidity varies across different trading sessions, impacting trade execution and order management. Market orders, limit orders, stop-loss orders, and trailing stops all behave differently depending on session activity. Understanding how these orders execute during high and low liquidity periods helps retail traders, hedge funds, and commercial banks manage risk efficiently.
Market Orders vs. Limit Orders: Execution Differences Across Sessions
Order execution speed and slippage depend on session liquidity. Traders choose between market orders for instant execution and limit orders for price-specific trades.
London-New York Overlap:
High liquidity ensures fast market order execution with minimal slippage.
Limit orders frequently fill at optimal prices, benefiting day traders and algorithmic trading strategies.
Asian Session:
Lower trading volume results in wider bid-ask spreads, impacting execution costs.
Market orders may experience slippage, especially in USD/JPY and AUD/USD pairs.
Late US Session to Sydney Open:
Limited liquidity affects order filling, making limit orders less reliable.
Traders using scalping strategies may encounter inconsistent execution speeds.
Selecting the right order type based on market timing ensures efficient trade execution and slippage reduction.
Stop Loss and Take Profit Strategies Based on Forex Market Hours
Effective stop-loss and take-profit placement depends on volatility and liquidity levels during different sessions.
| Trading Session | Volatility Level | Best Stop-Loss Strategy | Best Take-Profit Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| London Session | High | Tight stop-loss to protect against sharp reversals | Short take-profit targets due to strong trends |
| New York Session | High | Wider stop-loss to account for economic releases | Larger take-profit to capitalize on price swings |
| Asian Session | Low | Tight stop-loss due to slow price movements | Longer take-profit strategy for swing trades |
| London-New York Overlap | Very High | Adaptive stop-loss with trailing mechanisms | Dynamic take-profit levels based on momentum |
Placing stop-loss and take-profit orders according to session volatility improves trade management and risk mitigation.
Trailing Stop and Order Management During Session Transitions
Session overlaps present opportunities and risks, requiring adaptive trailing stop mechanisms for trade protection.
During Session Openings:
Increased volatility means wider trailing stops prevent premature trade exits.
Favorable for trend-following and news trading strategies.
Session Closures:
Liquidity drops lead to price stagnation, increasing stop-out risks.
Scalping and short-term trades benefit from tighter trailing stops.
High-Impact News Events:
Economic announcements cause price spikes, requiring wider trailing stops for protection.
Central bank decisions on interest rates and inflation reports significantly impact order execution.
Trailing stop adjustments ensure positions remain protected without being prematurely closed during price fluctuations.
Weekend Gaps and How Traders Manage Unfilled Orders
Forex markets close on Fridays at 22:00 GMT and reopen on Sundays at 22:00 GMT, causing price gaps when unexpected events occur.
Types of Weekend Gaps:
Bullish Gaps: A currency opens higher than Friday’s close due to strong economic data or geopolitical stability.
Bearish Gaps: A currency opens lower due to risk-off sentiment from events like elections, sanctions, or trade wars.
Managing Unfilled Orders:
Limit Orders: Orders placed before the weekend may not execute at expected prices due to gaps.
Stop-Loss Orders: Can be triggered at unfavorable prices, leading to higher slippage risk.
Hedging Strategies: Traders use currency pairs with negative correlations, such as USD/CHF and EUR/USD, to offset risk.
Adapting risk management approaches before market close minimizes potential losses from unexpected weekend price gaps.
Conclusion
The timing of the forex market plays a fundamental role in shaping liquidity, volatility, and strategic opportunities for traders. As different financial hubs open and close, market participants—including central banks, commercial institutions, and retail traders—respond to economic data releases and geopolitical developments that drive price movements. The interplay between session overlaps, interest rate decisions, and economic indicators determines the most active trading periods, offering both opportunities and risks.
Understanding when the market opens and how its structure influences currency price fluctuations allows traders to refine their strategies. Whether using trend-following methods, scalping techniques, or news-based approaches, aligning trading activities with optimal market hours enhances decision-making and efficiency. Awareness of liquidity shifts, order execution timing, and macroeconomic influences ensures that traders remain well-prepared for fluctuating conditions. By leveraging market timing insights, traders can maximize their potential while managing risks effectively.
The forex market operates 24 hours a day, starting with the Sydney session, followed by Tokyo, London, and New York. Each session opens and closes at specific times depending on the time zone:
Overlaps between sessions, such as London-New York and Tokyo-London, are the most active trading periods.
Sydney: 10:00 PM – 7:00 AM GMT
Tokyo: 12:00 AM – 9:00 AM GMT
London: 8:00 AM – 5:00 PM GMT
New York: 1:00 PM – 10:00 PM GMT
The impact of market participants varies based on their trading behavior and objectives:
Central banks influence liquidity through monetary policy decisions.
Hedge funds and investment managers drive large-volume trades, affecting volatility.
Retail traders are more active during high-volatility hours, particularly during session overlaps.
Certain economic indicators create significant movements in currency prices when released during active trading sessions. The most influential include:
Interest rate decisions from central banks
Inflation rate reports, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI)
GDP growth announcements, which affect long-term currency trends
Unemployment rate data, influencing central bank policy expectations
The most suitable trading time depends on the strategy being used:
Scalping and day trading: Best during high-liquidity periods, such as the London-New York session overlap.
Swing trading: Effective when price momentum builds, often at session openings and closings.
Carry trade: Ideal in stable market conditions with low volatility, often during quieter sessions.
The execution of order types is influenced by market liquidity and session activity:
Market orders execute instantly but may experience slippage in low-liquidity hours.
Limit orders ensure specific entry points, useful when anticipating price movements during news releases.
Stop-loss orders help protect against sudden volatility spikes that occur at market openings.
Major geopolitical events can disrupt normal trading patterns and increase volatility in specific sessions. Events such as elections, trade wars, and political instability often lead to sharp currency fluctuations. When such events coincide with major market openings, price swings can be more pronounced, creating both risks and trading opportunities.


