Table of contents
Navigating the world of forex trading can feel overwhelming at first, especially when faced with complex market visuals. Forex charts play a crucial role in helping traders interpret price movements and make informed decisions. Understanding how to read these charts allows beginners to track currency pairs like EUR/USD or USD/JPY, recognize trends, and identify trading opportunities. By learning the key elements of forex charts—such as chart types, technical indicators, and patterns—new traders can gain the confidence to analyze market behavior effectively. Developing this skill is essential for anyone looking to succeed in the fast-paced environment of forex trading.
Types of Forex Charts Explained
Understanding forex charts is fundamental for analyzing currency pairs like EUR/USD and USD/JPY. Mastering different chart types improves the ability to spot trends, track price action, and develop trading strategies effectively.
Candlestick Charts: The Most Popular Forex Chart Type
Candlestick charts remain the primary tool for forex traders seeking a visual, detailed snapshot of market sentiment. Each candlestick reflects four crucial data points: the opening, closing, high, and low prices within a specific time frame, whether it's a 1-minute chart or a Daily chart.
Key Elements of Candlestick Charts:
Open: The price at which the currency pair began the selected time frame (e.g., GBP/JPY on a 4-hour chart).
Close: The price at the end of the period, revealing bullish or bearish dominance.
High/Low: The highest and lowest prices during the time frame.
Body and Wicks: Visual indicators of market pressure; longer wicks often suggest volatility.
The ability to recognize patterns like Doji, Hammer, and Engulfing through candlestick charts aids traders in identifying potential reversals or continuations, especially in volatile conditions.
How to Read Line Charts in Forex Trading
A line chart simplifies price action by connecting closing prices of currency pairs such as USD/CAD or EUR/GBP over a defined period. Despite its simplicity, understanding line charts equips traders with a clean, clutter-free view of long-term trends, particularly useful when avoiding noise caused by short-term fluctuations.
Steps to Read Line Charts Effectively:
Select a Relevant Time Frame: Use shorter periods (e.g., 15-minute, 1-hour) for intraday trading and longer ones (Daily, Weekly) for broader trend analysis.
Focus on the Closing Price: This filters out intraday volatility.
Identify Clear Trend Directions: Upward, downward, or ranging markets.
Cross-reference with Technical Indicators: Moving Averages confirm patterns.
Apply Insights to Popular Pairs: Use EUR/USD or NZD/USD to evaluate market sentiment.
Understanding Bar Charts for Forex Traders
Bar charts offer a balanced view of market data, showing the open, high, low, and close prices, similar to candlesticks but with a distinct visual style. Each bar covers a specific time frame—1-hour, 15-minute, or even Monthly—and helps traders assess price ranges and volatility across currency pairs.
Here’s a comparative table to illustrate key differences and attributes:
| Attribute | Bar Chart | Candlestick Chart | Line Chart |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Points | Open, High, Low, Close | Open, High, Low, Close | Close prices only |
| Visual Complexity | Moderate | High (visual appeal with colored bodies/wicks) | Low (simple lines) |
| Best Use Case | Volatile markets (USD/CHF, CAD/JPY) | Identifying patterns & sentiment shifts (EUR/JPY) | Long-term trend clarity (EUR/USD, GBP/JPY) |
| Time Frame Versatility | Suitable for all (1-minute to Monthly) | Highly adaptable across time frames | Primarily Weekly/Monthly for trend spotting |
| Pattern Recognition | Moderate, clearer for experienced traders | High, intuitive visual cues | Low, lacks detailed pattern information |
Mastering bar charts supports better decision-making when combining them with indicators like MACD or Bollinger Bands.
Heikin Ashi and Renko Charts: Advanced Visualizations
Advanced forex traders often leverage Heikin Ashi and Renko charts for clearer trend identification and noise reduction. Both chart types differ significantly from standard candlestick or bar charts by focusing on smoothed price action.
Heikin Ashi modifies candlestick calculations by averaging open and close prices, filtering out minor market fluctuations. This approach aids traders in identifying strong trending markets, whether bullish or bearish. On the other hand, Renko charts ignore time entirely, constructing "bricks" based solely on price movement size, making them invaluable for detecting breakout opportunities in consolidating conditions.
For traders analyzing volatile pairs like USD/JPY or CAD/JPY, combining Renko charts with technical indicators such as Average True Range or Ichimoku Cloud helps refine entry and exit strategies, particularly when markets shift between trending and ranging states.
Key Technical Indicators on Forex Charts
Technical indicators provide essential insights when analyzing forex charts. Mastering tools like Moving Averages, RSI, and MACD helps traders interpret currency pairs such as EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, or USD/JPY with precision.
Using Moving Averages to Identify Trends
Moving Averages smooth price data, helping traders recognize long-term trends across forex charts. They filter short-term price fluctuations, whether on a 5-minute or Daily chart, making market direction clearer.
Steps to Apply Moving Averages Effectively:
Select a Time Frame: Use shorter periods (e.g., 15-minute, 1-hour) for intraday trading and longer ones (Daily, Weekly) for broader trend analysis.
Choose Moving Average Type: Simple Moving Average (SMA) and Exponential Moving Average (EMA) are the most common.
Apply to Currency Pair: Popular pairs like USD/CAD or EUR/JPY work well.
Analyze Crossover Signals: When the short-term average crosses above the long-term, it suggests a bullish trend; a downward cross signals bearish conditions.
Confirm with Market Conditions: Ensure alignment with trending or consolidating phases.
Relative Strength Index (RSI) on Forex Charts
RSI gauges whether a currency pair is overbought or oversold. Presented on a scale of 0 to 100, values above 70 often indicate overbought conditions, while values below 30 point to oversold scenarios.
Traders monitoring RSI on pairs like AUD/USD or NZD/USD can spot potential reversal points. When combined with candlestick patterns such as Double Bottom or Head and Shoulders, RSI becomes even more powerful, confirming entry and exit decisions during volatile markets.
MACD: Reading Momentum and Divergences
The MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) indicator reflects momentum shifts by comparing short-term and long-term EMAs. Its histogram and signal line help visualize potential reversals and continuation patterns.
| MACD Element | Description | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Short-term EMA (12-period) | Captures recent price movement trends | Effective for EUR/USD on 1-hour charts |
| Long-term EMA (26-period) | Provides broader market perspective | Helps identify divergences on GBP/JPY, USD/CHF |
| Signal Line (9-period EMA) | Smooths MACD line for clearer entry signals | Bullish when MACD crosses above signal line |
| Histogram | Visual gap between MACD and Signal Line | Highlights momentum strength during volatility |
| Divergence | Price trend contrasts MACD trend; signals possible reversal | Used to anticipate trend shifts in USD/JPY |
Traders often integrate MACD with Fibonacci Retracement levels for added confirmation, especially during consolidating or trending market phases.
Fibonacci Retracement Levels in Forex Chart Analysis
The Fibonacci Retracement tool helps traders identify potential price correction levels after a strong move. It is built on ratios like 38.2%, 50%, and 61.8%, often applied across time frames from 1-hour to Daily charts.
For instance, when analyzing the EUR/USD pair after a bullish run, plotting retracement levels between recent highs and lows reveals zones where price might temporarily reverse. Many traders pair Fibonacci levels with chart patterns like Wedges or Flags, enhancing predictive accuracy.
Bollinger Bands: Measuring Volatility on Forex Charts
Bollinger Bands consist of three lines: a Simple Moving Average in the middle and two standard deviation bands above and below. They expand and contract based on market volatility.
When analyzing currency pairs like USD/JPY or CAD/JPY, Bollinger Bands reveal:
Periods of Low Volatility: Bands contract, signaling potential breakout.
Periods of High Volatility: Bands widen, suggesting caution.
Price Touching Bands: May indicate overbought or oversold conditions, especially when supported by RSI or MACD readings.
Applying Bollinger Bands on 30-minute or 4-hour charts allows traders to adapt strategies to prevailing market conditions, particularly in trending or ranging environments.
Essential Forex Chart Patterns for Beginners
Recognizing chart patterns empowers forex traders to anticipate price movements across currency pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/JPY. Understanding these patterns strengthens the ability to navigate bullish and bearish conditions confidently.
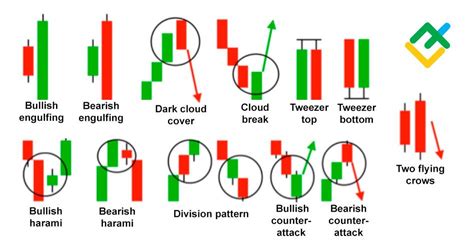
Recognizing Head and Shoulders Patterns
The Head and Shoulders pattern signals potential trend reversals, especially on Candlestick and Bar charts. Characterized by three peaks, the middle being the highest, this formation often appears after bullish runs.
Components of Head and Shoulders:
Left Shoulder: First peak, followed by a decline.
Head: Highest peak, surpassing the shoulders.
Right Shoulder: Lower peak, similar to the left shoulder.
Neckline: Support level connecting the two troughs.
Traders analyzing pairs like USD/CAD or AUD/USD watch for a neckline break, indicating bearish momentum, particularly on 1-hour or Daily charts.
Double Top and Double Bottom: Reversal Signals
Price action often leaves clues in the form of Double Top and Double Bottom patterns. Both signal impending reversals and are identifiable across different time frames and chart types.
Double Top:
Appears after bullish trends.
Two peaks at similar price levels.
Break below the support line indicates bearish reversal.
Double Bottom:
Forms after bearish trends.
Two troughs at similar price levels.
Break above resistance signals bullish reversal.
Pairs like EUR/GBP and NZD/USD commonly exhibit these patterns, especially during consolidating market conditions.
Triangle Patterns: Continuation and Breakout Strategies
Triangle patterns compress price action before sharp breakouts. Three primary types exist:
| Triangle Type | Shape Description | Market Condition | Common Currency Pairs | Time Frames |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending Triangle | Flat resistance, rising support | Bullish | EUR/USD, USD/JPY | 1-hour, 4-hour |
| Descending Triangle | Flat support, falling resistance | Bearish | GBP/JPY, USD/CHF | Daily, Weekly |
| Symmetrical Triangle | Converging trendlines | Neutral, Breakout Pending | AUD/USD, CAD/JPY | 15-minute, 1-hour |
Traders often combine Triangle patterns with indicators like MACD or RSI to confirm breakout directions.
Flags and Pennants: Short-Term Trading Setups
Flags and Pennants are ideal for short-term strategies, especially during volatile market phases. After a strong price movement (flagpole), a brief consolidation follows before continuation.
Flags:
Rectangular shape.
Sloped counter-trend consolidation.
Best spotted on 5-minute, 15-minute charts (e.g., USD/JPY, EUR/JPY).
Pennants:
Small symmetrical triangles.
Appear after sharp moves.
Signals breakout continuation in trending markets.
Combining these setups with Bollinger Bands enhances timing accuracy.
Wedges and Market Trend Shifts
Wedges differ from triangles by their slanting formation and predictive nature. Falling Wedges often lead to bullish breakouts, while Rising Wedges signal bearish shifts. These patterns frequently occur in pairs like USD/CHF and GBP/JPY, visible on Candlestick charts.
The sloping trendlines converge, reflecting shrinking volatility before a decisive price move. Pairing wedge patterns with Average True Range and Fibonacci Retracement helps traders gauge breakout strength, particularly in consolidating or volatile conditions.
Cup and Handle: Identifying Bullish Formations
The Cup and Handle pattern signifies bullish continuations, especially during trending markets.
A rounded "cup" forms after a period of consolidation, followed by a slight downward "handle" before a breakout. Traders often spot this on 4-hour and Daily charts for pairs like EUR/USD and USD/CAD.
Visualizing the pattern:
Cup: Smooth, rounded bottom indicating gradual recovery.
Handle: Brief pullback forming a downward drift.
Breakout: Price breaks resistance, signaling strong upward momentum.
Confirming the Cup and Handle with indicators like Parabolic SAR or On Balance Volume increases trade confidence, particularly in bullish market conditions.
Forex Chart Time Frames and Trading Strategies
Choosing the right time frame on forex charts influences trading strategies and risk management. Whether focusing on EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, or USD/JPY, matching time frames to goals shapes consistent performance.
Choosing the Right Time Frame: 1-minute to Monthly
Selecting an appropriate time frame depends on trading style, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Each forex chart time frame—from 1-minute to Monthly—offers unique advantages.
1-minute and 5-minute charts: Suitable for scalpers targeting minor price shifts in volatile pairs like USD/CHF or CAD/JPY.
15-minute and 30-minute charts: Balance quick trades with clearer trend signals, ideal for intraday setups.
1-hour and 4-hour charts: Offer broader trend views; useful when analyzing technical indicators such as MACD or RSI on pairs like AUD/USD and EUR/JPY.
Daily, Weekly, Monthly charts: Favored by swing and position traders seeking major trend movements, often pairing them with chart patterns like Wedges or Double Tops.
Aligning Moving Averages and Fibonacci Retracement tools across time frames ensures better trade execution.
Intraday Trading Using 5-minute and 15-minute Charts
Intraday traders rely heavily on lower time frames, focusing on quick entries and exits. Pairs like EUR/USD, USD/CAD, and GBP/JPY are often preferred due to liquidity and volatility.
Steps to Execute Intraday Trades Effectively:
Select a 5-minute or 15-minute chart for target currency pairs.
Apply key indicators: Bollinger Bands, Relative Strength Index, and Moving Averages assist in confirming entry points.
Identify patterns: Look for short-term formations like Flags and Pennants.
Use tight stop-loss levels to control risk in volatile sessions.
Monitor market conditions: Be aware of consolidating or trending phases to avoid false breakouts.
Consistent analysis of chart patterns and market shifts across intraday time frames maximizes precision.
Swing Trading with Daily and Weekly Forex Charts
Swing trading emphasizes capturing medium-term price movements, often lasting days or weeks. Traders using Daily and Weekly charts gain a broader perspective, reducing the impact of minor volatility.
Currency pairs like USD/JPY and EUR/GBP often exhibit clearer patterns on these higher time frames. Recognizing setups such as Head and Shoulders or Cup and Handle becomes easier, particularly when combined with technical indicators like Parabolic SAR or Ichimoku Cloud.
The advantage of using Daily and Weekly charts lies in their alignment with market cycles. Consolidating conditions become more apparent, and trend direction is more reliable. This method suits traders who prefer holding positions longer, avoiding the noise of 1-hour or 15-minute charts, while still leveraging tools like Fibonacci Retracement to refine entry and exit levels.
Interpreting Market Conditions on Forex Charts
Forex charts reveal critical clues about market conditions. Recognizing patterns across currency pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/JPY helps traders adapt to bullish, bearish, ranging, or volatile environments.
Identifying Bullish vs. Bearish Markets Through Charts
Understanding the distinction between bullish and bearish markets is vital when analyzing forex charts. Indicators and chart patterns assist in recognizing these conditions across various time frames.
Bullish Market Characteristics:
Price consistently forms higher highs and higher lows.
Moving Averages slope upward, particularly on Daily and Weekly charts.
Candlestick formations like Cup and Handle or Double Bottom confirm bullish momentum.
RSI often reads below 70 but remains elevated.
Common in currency pairs such as AUD/USD or EUR/JPY during strong economic cycles.
Bearish Market Characteristics:
Lower highs and lower lows dominate price action.
Indicators like MACD show negative divergence.
Patterns such as Head and Shoulders and Falling Wedges reinforce bearish sentiment.
RSI frequently drops below 30 in oversold conditions.
Typically observed in USD/CAD or USD/CHF during downturns.

Recognizing Ranging and Consolidating Market Phases
Ranging and consolidating phases reflect periods where price oscillates within tight support and resistance levels. Traders using Bar charts or Heikin Ashi charts identify these zones to avoid false breakouts.
Key Signals of Ranging Markets:
Price moves sideways without clear direction on 1-hour or 4-hour charts.
Bollinger Bands narrow, reflecting low volatility.
Indicators like Stochastic Oscillator fluctuate around mid-levels.
Candlestick patterns show indecision—frequent Doji or small-bodied candles.
Common in EUR/GBP and NZD/USD pairs, especially before major economic events.
How Volatility Appears on Forex Charts
Volatility can shape trading strategies significantly. It becomes visible across different chart types and indicators, especially during news releases affecting pairs like GBP/JPY or USD/JPY.
| Volatility Indicators | Description | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bollinger Bands | Bands widen during high volatility | Useful for spotting breakouts on AUD/USD or USD/CHF |
| Average True Range (ATR) | Measures average range between highs and lows | Applied on 15-minute or 1-hour charts for day trading |
| Candlestick Patterns | Long wicks and large bodies indicate sudden price moves | Spotted in volatile markets like CAD/JPY |
| MACD Histogram | Sharp increases or decreases signal momentum surges | Ideal for 4-hour charts analyzing USD/CAD or EUR/USD |
| Price Gaps | Visible gaps between sessions reflect volatility | Noted on Weekly charts, especially post-news events |
Mastering these signals helps traders adjust position sizes and stop-loss levels appropriately.
Detecting Overbought and Oversold Conditions
Overbought and oversold conditions suggest potential price reversals. Technical indicators like Relative Strength Index (RSI) and Stochastic Oscillator reveal these zones across forex charts.
Overbought Conditions:
RSI values above 70.
Currency pairs such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY exhibit prolonged bullish runs.
Frequently appears after bullish chart patterns like Triangle breakouts.
Oversold Conditions:
RSI readings below 30.
Bearish market conditions on pairs like USD/JPY or NZD/USD.
Often seen after sustained downward trends and consolidation phases.
Combining RSI signals with chart patterns like Double Bottom improves accuracy in volatile environments.
Trending vs. Sideways Markets: Adapting Chart Analysis
Market conditions constantly shift between trending and sideways phases, each demanding specific analysis methods. A trending market, whether bullish or bearish, reveals strong momentum, while sideways markets reflect indecision and low volatility.
Traders analyzing Daily or Weekly forex charts for pairs like USD/CHF or CAD/JPY monitor Moving Averages for trend confirmation. Trending phases are reinforced by chart patterns such as Wedges or Flags, while sideways markets show narrow price ranges, supported by tightening Bollinger Bands and neutral MACD signals.
Recognizing these shifts enables traders to adjust strategies, switching from trend-following approaches to range-bound tactics based on evolving market conditions.
Common Mistakes When Reading Forex Charts
Missteps when reading forex charts often stem from misunderstanding market conditions, indicators, and time frames. Avoiding these common mistakes can improve strategy when analyzing EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, or USD/JPY.
Overcomplicating Forex Chart Analysis
One of the biggest traps for beginners is cluttering forex charts with too many indicators and tools. This often leads to analysis paralysis.
Typical signs of overcomplication:
Using multiple indicators like MACD, RSI, Ichimoku Cloud, Bollinger Bands, and Parabolic SAR simultaneously without clear purpose.
Switching between different chart types—Candlestick, Heikin Ashi, Renko—frequently, causing conflicting signals.
Monitoring too many currency pairs at once (e.g., USD/CHF, CAD/JPY, AUD/USD), leading to scattered focus.
Simplifying by focusing on one or two indicators and a single time frame (like 1-hour or 4-hour charts) enhances clarity and decision-making.
Ignoring Market Conditions and Chart Patterns
Chart patterns and prevailing market conditions are critical when reading forex charts. Overlooking these leads to poor trade timing.
Trending Markets:
Indicators like Moving Averages and MACD help confirm direction.
Ignoring patterns like Triangle or Wedge formations causes missed opportunities.
Ranging Markets:
Consolidation phases often display Double Top or Double Bottom patterns.
Failure to recognize support and resistance levels on Bar charts risks unnecessary losses.
Volatile Conditions:
Patterns like Flags and Pennants paired with ATR reveal breakout potential.
Overlooking such setups can result in missed trades on pairs like EUR/GBP or NZD/USD.

Misinterpreting Technical Indicators
Incorrect use of indicators skews forex chart analysis, particularly for currency pairs like USD/CAD or EUR/JPY. Different indicators serve distinct purposes, yet traders often misread their signals.
| Technical Indicator | Common Misinterpretation | Correct Usage Example |
|---|---|---|
| Relative Strength Index | Overreliance on RSI without checking price action | Confirm overbought on GBP/JPY with Candlestick patterns |
| Moving Average | Assuming crossovers always signal trend reversals | Use crossovers with MACD on 4-hour charts for EUR/USD |
| Bollinger Bands | Misreading band expansion as immediate breakout | Confirm with Volume indicators on USD/CHF or AUD/USD pairs |
| Fibonacci Retracement | Blindly placing retracement levels without trend context | Apply retracement levels after strong moves on EUR/JPY |
Understanding each indicator’s context within time frames like Daily or 15-minute charts avoids costly errors.
Failing to Align Time Frames with Trading Goals
Mismatching trading goals and time frames often results in inconsistency. A trader aiming for quick profits shouldn’t rely on Monthly charts, just as a swing trader gains little from 1-minute analysis.
For example, scalpers focusing on pairs like USD/JPY or GBP/JPY typically use 5-minute or 15-minute charts, applying Bollinger Bands or RSI to spot immediate price shifts. Meanwhile, position traders analyzing Weekly charts prefer patterns such as Head and Shoulders or Cup and Handle on pairs like EUR/USD or USD/CAD, ensuring long-term market alignment.
Balancing technical indicators and chart types with suitable time frames strengthens strategy consistency across bullish, bearish, or consolidating conditions.
Conclusion
Mastering the ability to read forex charts transforms the way traders approach the foreign exchange market. From decoding candlestick formations to recognizing the significance of technical indicators like the Moving Average or Relative Strength Index, every element on a forex chart provides valuable insight into price dynamics. Grasping chart patterns such as Head and Shoulders or Double Tops, selecting appropriate time frames, and interpreting market conditions such as bullish trends or consolidating phases all contribute to a sharper analytical edge. By avoiding common mistakes and continuously refining chart-reading skills, traders position themselves to respond effectively to shifting market scenarios and improve their overall trading performance. A strong foundation in reading forex charts is not just useful—it is indispensable for long-term success.
The most widely used types of forex charts include:
Candlestick charts are the most popular because they offer clear visual cues on price action and market sentiment.
Candlestick charts
Line charts
Bar charts
Heikin Ashi charts
Technical indicators provide additional layers of analysis that complement price movements seen on forex charts. Tools like the MACD and Bollinger Bands help traders identify momentum, trend strength, and potential reversal points. Indicators simplify complex market data, allowing traders to make more calculated decisions.
The ideal time frame depends on a trader’s goals and strategy. Beginners often start with:
Experimenting with different time frames helps beginners align their strategy with their trading style.
1-hour charts for manageable short-term analysis
Daily charts to understand broader trends
15-minute charts for intraday practice
Chart patterns serve as visual signals that can predict future price direction. Recognizing patterns like Wedges, Triangles, or Cup and Handle formations enables traders to anticipate potential breakouts or reversals. Integrating these patterns with technical indicators can improve entry and exit timing.
Some of the common errors include:
Avoiding these pitfalls strengthens overall chart interpretation.
Overcomplicating analysis with too many indicators
Ignoring the broader market conditions
Misinterpreting short-term signals without context
Failing to align time frames across analysis
Traders frequently analyze major currency pairs due to their liquidity and volatility:
These pairs often produce clearer trends and patterns, making them ideal for chart analysis.
EUR/USD
GBP/JPY
USD/CAD
AUD/USD
USD/CHF
Market conditions play a crucial role in chart analysis. During volatile periods, price swings appear more pronounced, making patterns and indicator signals more sensitive. Traders must adjust their strategies based on whether the market is trending, consolidating, or experiencing high volatility to interpret forex charts effectively.


