Table of contents
Getting started with online trading can feel overwhelming, especially when dealing with international markets. Forex trading offers individuals in India the opportunity to engage with global currency markets and potentially grow their capital through strategic buying and selling. With increasing accessibility and awareness, more Indian traders are exploring how currency pairs like USD/INR, EUR/USD, and GBP/JPY move in response to global economic shifts. Understanding the core concepts, legal considerations, and practical tools involved is essential before placing a single trade. Whether you're aiming for short-term gains or long-term strategies, building a solid foundation is the first step toward navigating the forex market with confidence.
Starting Forex Trading in India
Understanding the entry points into forex trading begins with clarity on rules, accessibility, and essential requirements.

Is Forex Trading Legal in India? What Every Trader Must Know
The legality of forex trading in India rests on specific boundaries set by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and enforced by SEBI. Trading in currency pairs that involve the Indian Rupee and are listed on authorized exchanges like NSE and BSE is permitted. However, direct trading through international platforms involving cross-currency pairs such as EUR/USD or GBP/JPY is considered illegal for retail traders unless routed through authorized Indian intermediaries.
This framework is governed by the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). Any violation—such as using an offshore broker for high-leverage trades in non-INR pairs—may lead to legal complications. Traders looking to engage in legal forex activities must stay within the regulatory scope that allows only exchange-traded contracts in permitted currency pairs like USD/INR, EUR/INR, GBP/INR, and JPY/INR. These contracts operate within a regulated structure, and trades are cleared via Indian clearing corporations.
Understanding this legal boundary is the first essential step before committing any funds or opening accounts.
How to Choose an RBI-Compliant Forex Broker
Select brokers registered with SEBI and offering access to currency derivatives listed on Indian exchanges (NSE, BSE, MSEI).
Avoid platforms offering cross-currency trading on high leverage outside Indian jurisdiction—these are not permitted for Indian residents.
Prioritize brokers providing access to INR-paired instruments, including USD/INR and EUR/INR.
Look for transparent brokerage fees, integration with banking channels, and fast KYC verification.
Evaluate platform performance, mobile trading features, and support for order types like Market Orders and Stop Loss Orders.
Features of RBI-Compliant vs. Non-Compliant Brokers
| Criteria | RBI-Compliant Broker | Non-Compliant Offshore Broker |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Body | SEBI | Unregulated or Foreign (e.g., CySEC) |
| Currency Pairs Available | INR-Paired Only (e.g., USD/INR) | Cross-Currency (e.g., EUR/USD) |
| Legal for Indian Residents? | Yes | No |
| Leverage | Limited (1:10 or lower) | Often very high (1:200 or more) |
| KYC Verification | Mandatory, Aadhaar-linked | Often skipped or minimal |
| Order Type Support | Market, Limit, Stop Loss | Varies widely |
Creating a Forex Trading Account from India: Step-by-Step
<step 1> Choose a SEBI-registered broker that offers access to Indian exchanges.
<step 2> Complete the online application, entering PAN, Aadhaar, and bank details.
<step 3> Upload proof of identity, address, and bank account ownership.
<step 4> Perform video KYC verification as per SEBI norms.
<step 5> Link your bank account to your trading wallet for deposits and withdrawals.
<step 6> Once verified, log in to your trading platform and access INR currency derivatives.
This process allows Indian residents to legally participate in forex trading under the RBI’s framework, focusing on permitted pairs like GBP/INR and JPY/INR.
Documents and KYC Requirements for Indian Forex Traders
Opening a legal forex account in India requires compliance with strict KYC norms. The verification process is designed to align with FEMA and SEBI guidelines and helps ensure the integrity of trading platforms.
PAN Card: Mandatory for tax tracking and trading authorization.
Aadhaar Card: Essential for identity verification and eKYC linkage.
Recent Photograph: A passport-sized image in digital format.
Bank Account Proof: Canceled cheque or bank statement with IFSC.
Address Proof: Utility bill, Aadhaar, or driving license (not older than 3 months).
After submitting documents, traders typically go through video-based verification. This process confirms identity through facial recognition and cross-verifies with provided documents. Approval times vary, but most Indian brokers complete onboarding within 24–48 hours.
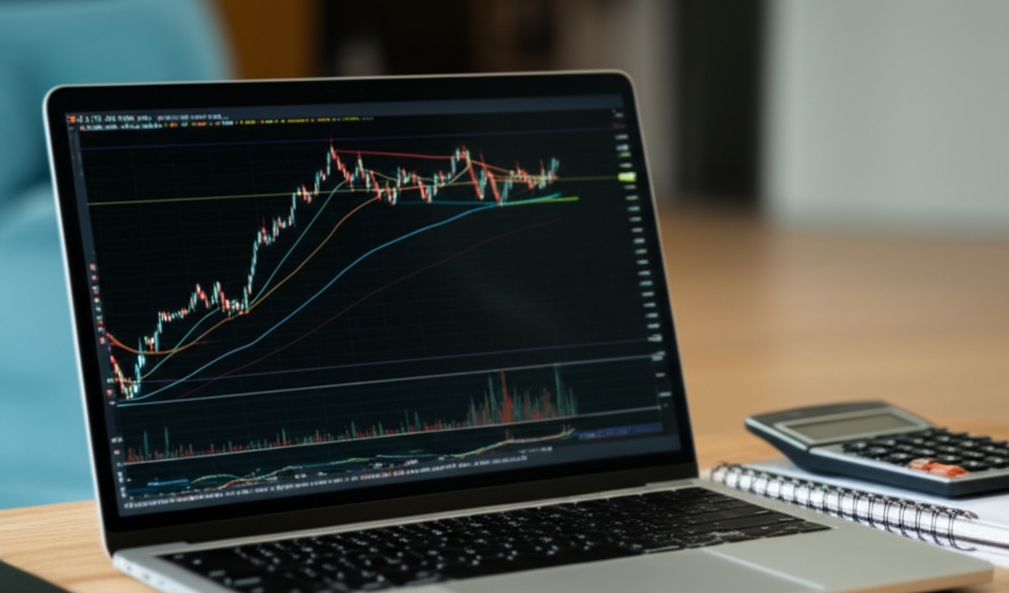
Understanding the Forex Market
Building a successful trading journey means mastering key market behaviors, patterns, and conditions that shape forex decisions.
What Are Currency Pairs and How They Work
Currency pairs are the core instruments used in forex trading. Each pair represents the relative value of one currency against another. For example, when trading EUR/USD, you're speculating on the value of the euro versus the US dollar. These pairs are categorized into three main types:
Major Pairs: Always include the USD, such as GBP/USD, USD/JPY, or EUR/USD. These have high liquidity and lower spreads.
Minor Pairs: Include strong currencies without the USD, like EUR/GBP or EUR/JPY. These tend to have slightly wider spreads.
Exotic Pairs: Involve a major currency and a developing or low-volume currency, such as USD/INR or EUR/TRY.
Traders must understand how these pairs respond to economic indicators like GDP, interest rate decisions, and inflation data. Price fluctuations in pairs like USD/CAD or AUD/USD are often tied to commodity trends, while safe havens like USD/CHF react to global uncertainty. Recognizing how pairs behave across different market conditions provides a tactical edge when timing trades.
Major vs. Minor Pairs: Which Ones Are Best for Indian Traders
Major Pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD, USD/JPY)
High liquidity
Narrow bid-ask spreads
Abundant economic data coverage
Minor Pairs (e.g., EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY, AUD/JPY)
Moderate liquidity
Higher volatility potential
Can react differently during Asian trading hours
Best Options for Indian Traders
Focus on INR pairs (USD/INR, EUR/INR) for compliance
For global exposure, practice on demo accounts with EUR/USD or GBP/JPY
Monitor economic events like the Consumer Price Index and Trade Balance announcements
| Pair Type | Example | Liquidity | Spread | Suitability for Indian Traders |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major | EUR/USD | Very High | Low | Excellent for beginners |
| Minor | EUR/GBP | Moderate | Medium | Good with strategy focus |
| INR-Paired | USD/INR | Regulated use | Low | Required for compliance |
| Exotic | USD/ZAR | Low | High | High-risk, not recommended |
Forex Market Conditions Explained: Bull, Bear, and Sideways
The mood of the forex market changes constantly. Recognizing its current state is essential for choosing the right entry and exit strategy.
Bull Market
Characterized by rising prices
Suitable for trend-following strategies like Position Trading
Often driven by strong GDP growth, lower Unemployment Rate, or positive interest rate changes
Bear Market
Marked by falling prices across currency pairs
Reversal Trading or short-selling strategies are more common
Indicators like the Relative Strength Index and Stochastic Oscillator often show oversold signals
Sideways Market
Prices move within a narrow range
Best for Range Trading and Scalping
Consolidation Phase often leads to an upcoming breakout
Understanding these conditions helps traders better align their tools, such as Moving Averages or Bollinger Bands, with market momentum.
How Forex Prices Are Influenced by Global Events
Exchange rates reflect real-time global sentiment. When major economies shift, currency values follow. A rise in US Interest Rates often strengthens the USD across pairs like USD/JPY or USD/CHF. Conversely, escalating geopolitical tensions may weaken high-risk currencies while boosting safe havens. For example, a change in the Inflation Rate in the Eurozone can influence EUR/USD movement. Unexpected unemployment data from the US can rattle markets, especially in volatile market conditions. News-driven spikes often lead to short-term trend changes, confirmed by technical tools such as the Ichimoku Cloud or MACD. Understanding this relationship lets traders anticipate direction, rather than simply react.
Trading Hours and Sessions for Forex in IST
Forex operates 24 hours a day, divided into overlapping global sessions. Timing can influence liquidity and volatility, especially for pairs like GBP/USD or AUD/USD. Below is a breakdown adapted to Indian Standard Time (IST):
Sydney Session (2:30 AM – 11:30 AM IST)
Lower liquidity, good for AUD/NZD-focused traders
Tokyo Session (5:30 AM – 2:30 PM IST)
Active for JPY pairs like USD/JPY and GBP/JPY
London Session (12:30 PM – 9:30 PM IST)
Most active session for major pairs
Key for breakout traders and scalpers
New York Session (5:30 PM – 2:30 AM IST)
High volatility, especially during US economic releases
Synchronizing your trading strategy with optimal market activity ensures better execution and tighter spreads.
Understanding Leverage and Margin in Forex Trading
Forex trading allows traders to control larger positions with smaller capital outlays using leverage. However, while leverage amplifies potential returns, it also increases the risk of losses.
A leverage ratio of 1:10 means ₹10,000 in capital can control a ₹1,00,000 position in pairs like EUR/USD or USD/INR. Brokers also apply margin requirements—essentially a security deposit—to open trades. For example, with 5% margin on a ₹1,00,000 position, a trader needs to maintain ₹5,000 in the account.
The risk lies in price volatility. A sharp move in a currency pair such as GBP/USD can trigger a Margin Call, leading to forced liquidation. Using tools like Stop Loss Orders and calculating position size using the Average True Range can help manage exposure. Indian traders must also respect SEBI leverage caps and understand that using margin responsibly is not about maximizing position size, but preserving long-term capital.
Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Decoding price behavior through tools like indicators, chart patterns, and market reactions sharpens decision-making in forex trading.
How to Use Moving Averages to Identify Trends
Moving Averages help traders smooth out price data and spot momentum direction over time. When properly applied, they reveal Bull Market or Bear Market conditions and support Trend Following strategies across pairs like EUR/USD or GBP/JPY.
Simple Moving Average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific period (e.g., 50-day or 200-day).
Exponential Moving Average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices, offering quicker signals.
A Golden Cross occurs when a short-term MA (e.g., 50-day) crosses above a long-term MA (e.g., 200-day), often signaling a Bull Market.
A Death Cross suggests the opposite — a potential Bear Market reversal.
MAs also serve as dynamic support and resistance zones in a Trending Market.
These indicators become especially powerful when paired with others like MACD or RSI, reinforcing entry or exit timing during a Breakout or a Consolidation Phase.
Interpreting RSI and MACD for Entry Signals
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Measures overbought and oversold conditions
Readings above 70 suggest Overbought Conditions (possible reversal)
Below 30 may indicate Oversold Conditions and potential entry points
MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)
Helps spot trend direction and momentum
Signal Line crossovers can trigger Buy or Sell signals
Histogram divergence from price may indicate weakening trend
Combination Use
Confirm MACD crossovers with RSI entering favorable zones
Avoid false signals during high Volatile Market periods
| Indicator | Use Case | Strength | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| RSI | Measures momentum | Simple to read | Lags in rapid price moves |
| MACD | Trend confirmation & timing | Versatile | Late signals in Sideways Markets |
| Combo | Entry validation | Increases accuracy | Requires experience to interpret |
Recognizing Chart Patterns: Triangle, Head and Shoulders, and Flags
Visual patterns on price charts are signals waiting to be interpreted. Traders develop a trained eye for formations like the Head and Shoulders, Triangles, or Flags, especially when combined with key Technical Indicators or Order Types.
In a typical Head and Shoulders pattern, the market sets a high (left shoulder), a higher high (head), and a lower high (right shoulder). A neckline forms the base, and its break often leads to sharp downward moves.
Triangles, whether ascending, descending, or symmetrical, suggest potential Breakout Trading opportunities. A breakout past the upper line during a Bull Market signals trend continuation.
Flags occur after a sharp move and involve slight consolidation, offering traders an entry point as the trend resumes.
Such patterns often appear during key sessions — London or New York — where volume can drive strong moves in pairs like USD/JPY or AUD/USD.
Using Bollinger Bands in a Volatile Market
Consist of three lines: middle band (usually a 20-day SMA), upper band, and lower band
Measure Volatility through standard deviations around the middle band
Squeeze Formation signals upcoming volatility expansion
Price touching upper band = Overbought Condition (potential reversal or breakout)
Price bouncing off lower band = Oversold Condition (possible recovery)
Works well with Stop Loss Orders placed just outside the bands during Scalping or Reversal Trading
Useful in currency pairs like GBP/USD or NZD/USD that often face sudden macro shifts due to economic reports such as Retail Sales or Trade Balance data
Fibonacci Retracement Levels for Identifying Pullbacks
Traders often search for retracement zones where price may pause or reverse. Fibonacci Retracement offers a roadmap.
A rally in EUR/JPY might begin to decline, yet rather than panicking, experienced traders look for bounce points near 38.2%, 50%, or 61.8% levels. These levels serve as dynamic support or resistance during a Consolidation Phase or after Breakouts.
If a trader anticipates a long entry after a strong upward move, waiting for a pullback to the 50% retracement level before placing a Buy Limit Order can enhance precision and reduce risk. Combining this with confirmation from the Stochastic Oscillator or a candlestick pattern like a Doji strengthens the probability of success.
Fibonacci works best when integrated with broader market context — is the market trending or range-bound? Is there upcoming GDP data that may invalidate technical assumptions?
Recognizing the retracement zone not only refines entries but also assists in placing well-calculated Stop Loss Orders and defining Take Profit zones aligned with risk-reward targets.
Forex Trading Strategies
Execution begins when observation transforms into action. Strategy choice defines how a trader engages with the market across sessions and conditions.
Day Trading vs. Swing Trading: Choosing Your Style
Both styles require precision, but each demands a different mindset, risk tolerance, and rhythm. A trader selecting between Day Trading and Swing Trading must examine their time availability, emotional discipline, and adaptability to Volatile Market conditions.
Day Trading involves opening and closing positions within a single trading day, often on pairs like GBP/USD or USD/JPY, capitalizing on intraday volatility. It requires frequent monitoring, rapid decision-making, and tools like the MACD and Bollinger Bands to spot Breakouts or momentum shifts.
Swing Trading, on the other hand, targets price moves over days or weeks. Traders may rely more on the Fibonacci Retracement, Moving Averages, and chart patterns like Double Bottom or Flag. Swing Traders typically prefer a less time-intensive structure but must tolerate overnight exposure and news-driven gaps.
| Criteria | Day Trading | Swing Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | Minutes to hours | Days to weeks |
| Tools Used | MACD, RSI, Bollinger Bands | Fibonacci, Moving Averages, Chart Patterns |
| Currency Pairs | High liquidity (EUR/USD, GBP/JPY) | Broader set (NZD/USD, USD/CAD, EUR/JPY) |
| Exposure Risk | Lower (no overnight) | Higher (holds over sessions) |
| Ideal Conditions | Trending and volatile | Trending with pullbacks |
Breakout Trading: How to Ride Strong Market Moves
Step 1: Identify consolidation zones or range-bound phases using the Ichimoku Cloud or Bollinger Bands
Step 2: Wait for a Breakout — typically outside a Triangle or Rectangle chart pattern
Step 3: Confirm with volume or indicators like the On Balance Volume and Average True Range
Step 4: Enter with a Market Order or Buy Stop Order just above the resistance zone
Step 5: Use a Stop Loss Order below the recent support and trail with a Trailing Stop Order
Step 6: Exit using a Take Profit Order at a measured move projection or key Fibonacci extension level
Breakout trading is especially effective during London and New York sessions where economic indicators like Interest Rate decisions or Non-Farm Payroll reports often trigger strong directional moves in pairs like EUR/USD or USD/CHF.
Reversal Trading with Confirmation Indicators
In a market driven by trend exhaustion, reversal trading seeks to capture the turning point before a new direction unfolds. The art lies not in guessing but in confirming.
Consider a scenario in a Bear Market where the GBP/JPY shows a steep decline. As price nears a historically strong support level, the Relative Strength Index drops below 30, indicating an Oversold Condition. At the same time, a Hammer candlestick forms on the daily chart — a classic signal of potential reversal. However, caution is essential.
A skilled trader waits. As the MACD line begins to curve upward and the Stochastic Oscillator crosses the 20-level from below, the alignment of multiple indicators strengthens the case for a reversal. The trader places a Buy Limit Order just above the signal candle’s high and sets a Stop Loss Order slightly below the low, defining risk.
Confirmation indicators like MACD, RSI, and Fibonacci Retracement not only reduce emotional decision-making but also enhance confidence. Reversal trading is not about chasing the bottom but recognizing the buildup to a shift in momentum — a process, not a prediction.
Economic Fundamentals That Move Forex
Decoding why currency pairs rise and fall begins with understanding the economic forces that fuel the market’s momentum.
How GDP and Interest Rates Influence Currency Strength
When Gross Domestic Product (GDP) figures exceed expectations, investor confidence often strengthens the domestic currency. A strong GDP report typically signals economic health, making assets more attractive to foreign investors. This increases demand for the currency and can lift pairs like USD/JPY or EUR/USD during major releases.
Interest Rate decisions, often made by central banks, exert even more immediate impact. A hike in rates attracts capital inflow due to higher returns on government bonds and savings instruments. This dynamic strengthens the currency—especially when the rate change is unexpected. Conversely, a rate cut may signal economic softness, often leading to depreciation.
Consider a scenario: the Reserve Bank of Australia raises its rate while the European Central Bank holds steady. In response, the AUD/EUR may rise as traders shift capital toward the yield-advantaged currency. Interest Rate trends also influence longer-term strategies such as Carry Trade, where traders borrow in a low-rate currency (like JPY) and invest in high-rate ones (like NZD).
Interpreting CPI and Inflation Trends as a Forex Trader
Consumer Price Index (CPI) is a primary inflation gauge and directly affects Interest Rate outlooks
Rising CPI may lead to higher Interest Rates, strengthening currency pairs like GBP/USD or USD/CHF
Falling CPI often weakens currency value and suggests easing policy
Traders use Inflation Rate data alongside Technical Indicators to time entries or exits during high-volatility windows
Inflation surprises often cause sharp moves in major pairs during New York or London sessions
Impact of CPI on Currency Behavior
| CPI Trend | Market Reaction | Currency Impact | Strategy Triggered |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higher than forecast | Hawkish central bank expectations | Currency strengthens | Breakout Trading |
| Lower than forecast | Dovish outlook expected | Currency weakens | Reversal Trading |
| Stable with growth | Balanced monetary stance | Currency consolidates | Range Trading or Scalping |
Trade Balance and Currency Volatility Explained
The Trade Balance reflects the difference between exports and imports. A surplus indicates a country exports more than it imports, strengthening its currency through increased foreign demand. Conversely, a deficit can weaken currency value due to the need for foreign capital to cover the gap.
For example, if Japan reports a strong Trade Balance while the United States sees a deficit, traders may favor the JPY over the USD, causing movement in USD/JPY or EUR/JPY. The impact becomes more significant during Volatile Market conditions, especially if paired with data like Retail Sales or GDP growth.
Trade Balance reports often trigger strong intraday moves, especially when released alongside other Economic Indicators. Technical tools like the Average True Range and On Balance Volume help validate volatility spikes and confirm directional shifts.
Role of Unemployment Rate and PMI Reports in Forex
The Unemployment Rate reflects labor market health and influences monetary policy decisions. A falling rate generally supports currency strength, while rising unemployment signals weakness. Pairs like EUR/GBP or USD/CAD often react to labor data from their respective economies.
Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI)—both Manufacturing PMI and Services PMI—offers forward-looking insight into economic momentum. A PMI above 50 signals expansion; below 50 suggests contraction.
Forex traders monitor these reports closely:
Manufacturing PMI drives commodity-sensitive currencies like AUD/USD and NZD/USD
Services PMI affects developed economies’ consumer demand outlook
Unemployment Rate shifts impact expectations around Inflation Rate and Interest Rate changes
Combined, these reports build anticipation and move markets in both Breakout and Trending Market conditions. When synchronized with Technical Indicators like the Ichimoku Cloud or Parabolic SAR, they become powerful triggers for informed trading decisions.
Mastering Execution and Risk
Once a trader understands the charts and strategies, success depends on how decisions are made, controlled, and protected in real time.
Using Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders Wisely
Stop Loss and Take Profit Orders offer traders structured exits to control losses and lock in gains. Relying on emotion or hope often leads to costly mistakes, especially in Volatile Market environments.
Stop Loss Orders: Limit downside during news events or rapid reversals. Placing them below technical support zones or beyond a recent Fibonacci Retracement level ensures trades have breathing space without exposing too much capital.
Take Profit Orders: Help secure gains without constantly monitoring the trade. Ideal placements include just below resistance levels or key moving averages like the 200-period EMA.
Use the Average True Range (ATR) to set realistic risk/reward boundaries.
Avoid placing stops too tight in Trending Markets to prevent premature exits.
These orders help traders maintain discipline during emotional decision points and anchor risk around objective metrics.
Calculating Position Size for Capital Protection
Determine total capital available (e.g., ₹1,00,000).
Decide on maximum risk per trade (usually 1–2%, i.e., ₹1,000–₹2,000).
Measure distance between entry and Stop Loss Order in pips (e.g., 50 pips).
Calculate pip value based on the currency pair traded (varies for EUR/USD vs. GBP/JPY).
Adjust lot size so that a 50-pip loss equals the defined rupee risk.
| Pair | Pip Value (Standard Lot) | Typical Stop Loss (pips) | Risk/Trade (1%) | Position Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EUR/USD | $10 | 50 | ₹1,000 | 0.2 lots |
| GBP/JPY | ¥1,000 | 70 | ₹2,000 | 0.15 lots |
| USD/INR | ₹1,000 | 40 | ₹1,000 | 0.25 lots |
Position sizing isn’t just math—it’s risk discipline in action, anchoring decisions in logic, not emotion.
Emotional Discipline in Live Forex Trading
It starts innocently—a Stop Loss is hit on a trade in EUR/USD, and suddenly the brain starts spinning. The trader enters again, not out of strategy but frustration. This moment is where most accounts begin to bleed.
Staying grounded in high-pressure moments is about preparation, not reaction. A trader who plans exits before entry, who understands that not every setup works, and who respects market conditions—whether a Breakout or a Sideways Market—stays aligned with logic.
The temptation to widen a Stop Loss Order when price nears it, or to ignore a Take Profit signal because the market “feels strong,” is common. But the disciplined trader accepts small losses as tuition and focuses on the next high-quality opportunity. Emotional neutrality is built by journaling trades, reviewing performance, and operating from rules, not feelings.
Trailing Stops and Locking in Profits During a Trend
Step 1: Enter a position in a Trending Market based on confirmation from Moving Averages or MACD.
Step 2: Set an initial Stop Loss Order below a recent low (for long trades).
Step 3: As the trade moves in favor, adjust the Stop Loss to trail behind price by a set distance (e.g., 30 pips).
Step 4: Use Average True Range to calculate volatility-adjusted trailing levels.
Step 5: As the price continues rising, the trailing stop moves with it, preserving gains while letting the trend run.
Trailing Stop Orders protect against reversals without cutting profits short. Traders using this tool on high-momentum pairs like GBP/USD or AUD/USD during Breakout phases often see better trade longevity with controlled downside.
Avoiding Overtrading and Revenge Trading
Recognize Overtrading as frequent, impulsive entries driven by boredom or fear of missing out. It often leads to taking low-quality setups.
Understand Revenge Trading happens after a loss, where emotion—not strategy—dictates entries.
Combat both behaviors by setting a maximum number of trades per day and defining clear criteria for entry, such as RSI divergence or Double Top confirmation.
Use Trading Journals to track emotional triggers tied to impulsive actions.
Revisit a failed trade with logic, not anger—was the Stop Loss based on technical support, or was it arbitrarily placed? Did the setup align with the market condition, such as a Consolidation Phase or Breakout?
Mastery isn’t just about wins. It’s about knowing when not to trade—and walking away when needed to protect long-term capital.
Conclusion
Mastering forex trading requires more than just curiosity—it demands clarity, discipline, and a structured approach. For traders in India, the path involves understanding not only the global currency ecosystem but also the domestic regulatory landscape and the mechanics of trading platforms approved for use. From selecting compliant brokers to reading chart patterns like triangles and head and shoulders, every piece contributes to a sharper trading instinct. Technical indicators such as the Moving Average or Relative Strength Index offer signals, while economic factors like GDP, interest rates, and inflation help build the bigger picture behind price movement. Success in the forex market often hinges not on a single strategy, but on the ability to integrate market knowledge, emotional discipline, and risk control. With focused effort and the right insights, forex trading can evolve from a confusing landscape into a skill-driven opportunity.
Forex trading involves the exchange of one currency for another with the aim of making a profit from changes in exchange rates. In India, retail forex trading is allowed only through specific currency pairs approved by the Reserve Bank of India and must be conducted via SEBI-regulated brokers.
USD/INR (high liquidity, directly linked to the Indian economy)
EUR/USD (globally popular with tight spreads)
GBP/JPY (high volatility, suitable for experienced traders)
USD/JPY (strong correlation with global interest rates)
Moving Average: for trend confirmation
Relative Strength Index (RSI): for identifying overbought or oversold conditions
MACD: for spotting momentum shifts
Bollinger Bands: for measuring volatility
Chart patterns visualize price psychology and help forecast future movements. Patterns like the Double Top or Cup and Handle signal potential reversals, while Pennants and Flags often indicate trend continuations. Recognizing these patterns can improve entry and exit timing.
Market Order: executes instantly at current price
Stop Loss Order: limits potential losses
Take Profit Order: locks in gains at target level
Limit Order: sets a specific entry price below or above market
Market behavior determines which strategies perform best. For instance, breakout trading is more effective in a trending market, while range-bound systems work better during consolidation phases. Being able to identify whether conditions are bullish, bearish, or sideways is essential for aligning tactics.
GDP reports
Interest rate announcements
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Employment data (especially Non-Farm Payrolls in the US)
Swing trading is often the most practical. It allows for holding positions over several days, which fits well with people who can’t monitor charts full-time. This strategy uses both technical and fundamental analysis and works well in markets with identifiable short- to mid-term trends.


